Art of Healing Part Two: The Emotional Wheel
Humans have 27 distinct emotions (Cowen & Keltner, 2017): admiration, adoration, aesthetic appreciation, amusement, anger, anxiety, awe, awkwardness, boredom, calmness, confusion, craving, disgust, empathic pain, entrancement, excitement, fear, horror, interest, joy, nostalgia, relief, romance, sadness, satisfaction, sexual desire, surprise. Humans can also experience 34,000 distinguishable emotions - a combo of distinct emotions and 8 primary emotions: joy, sadness, acceptance, disgust, fear, anger, surprise, and anticipation.
Becoming aware of your emotional state helps you manage it better - also known as mindfulness. How can you visualize your negative emotions, and develop actionable steps or strategies to achieve the opposite?
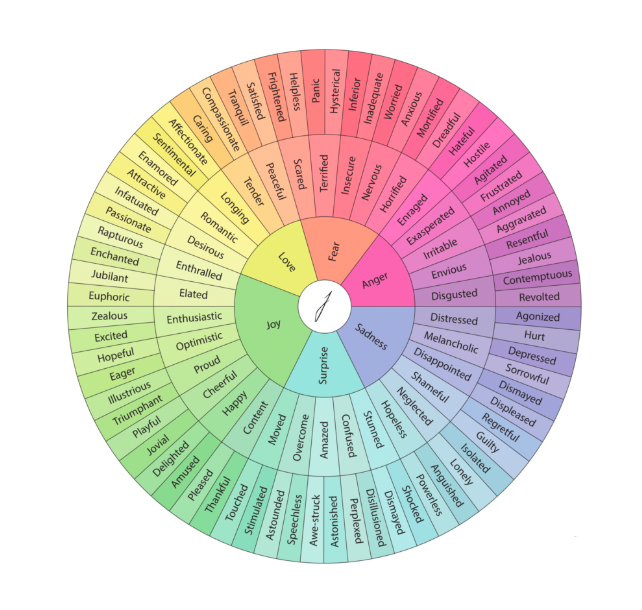
Gloria Wilcox developed the Feelings Color Wheel through inspiration from Robert Plutchik's version of Feeling’s Wheel, by breaking emotions into 6 main categories, then breaking them down into sub-categories. Gloria’s emotional color wheel is intended to help individuals better understand, communicate, and work through their emotions.
Print or reference the below sheet to help you navigate and develop more awareness of your emotions. This will help you build the tools to practice mindfulness and learn how to shift your emotions from negative to positive.
Questions you can ask to get started: Are you feeling Fear? What type of fear? Are you frightened or worried? What’s causing you to feel those elements? What can you do to move to the opposite direction? Are you feeling anxious? What is causing your anxiety? What can you do to reach a state of feeling content, delight, and gratitude?
Curious to learn more in depth? Continue reading further on below:
The Emotional Color Wheel creator, Plutchnik, grouped the primary 8 emotions into polar opposites:
Joy and Sadness
Acceptance and Disgust
Fear and Anger
Surprise and Anticipation
Plutchnik’s emotions theory is defined by 10 postulates:
Animals and Humans
The midbrain (or the limbic system) of a human is similar to that of other mammals. Animals and humans experience the same basic emotions.Evolutionary History
Emotions came into being as part of the evolutionary process, long before there were apes or humans.Survival Issues
The most influential role of emotions is to help us survive.Prototype Patterns
These are the common identifiable patterns and elements that make up each emotion.Basic Emotions
The most basic emotions are the primary ones: trust, fear, surprise, sadness, disgust, anger, anticipation and joy.Combinations
The adding up of these various primary emotions will produce new ones such as: love = (joy+ trust), guilt = (joy + fear), and delight = (joy + surprise).Hypothetical Constructs
Emotions are constructs, or ideas, that help describe a certain experience.Opposites
Like many things in nature, there is a duality with emotions, hence each one has its polar opposite:
– saddens is the opposite of joy
– trust is the opposite of disgust
– fear is the opposite of anger
– surprise is the opposite of anticipationSimilarity
The degree of similarity determines which emotions are more related, and which ones are the complete opposite.Intensity
This degree of change in intensity, from very strong to not so much, produces the diverse amount of emotions we can feel. Such as:
– trust goes from acceptance to admiration
– fear goes from timidity to terror
– surprise goes from uncertainty to amazement
– sadness goes from gloominess to grief
– disgust goes from dislike to loathing
– anger goes from annoyance to fury
– anticipation goes from interest to vigilance
– joy goes from serenity to ecstasy
The Emotional Color wheel also enables participants to visualize your emotions, and gain an understanding of where the emotions came from.
Plutchnik identified survival behaviors:
Protection: Withdrawal, retreat (activated by fear and terror).
Destruction: Elimination of barrier to the satisfaction of needs (activated by anger and rage).
Incorporation: Ingesting nourishment (activated by acceptance).
Rejection: Riddance response to harmful material (activated by disgust).
Reproduction: Approach, contract, genetic exchanges (activated by joy and pleasure).
Reintegration: Reaction to loss of nutrient product (activated by sadness and grief).
Exploration: Investigating an environment (activated by curiosity and play).
Orientation: Reaction to contact with an unfamiliar object (activated by surprise).
(Screenr, 2017)
Sources:
https://positivepsychology.com/emotion-wheel/
#ArtTherapy #ColorWheel #Art #Emotions